Even with the growing popularity of chat platforms, most people continue to depend on email for a wide range of things. When it comes to setting up an email account, there are two main types to choose from – email clients and webmail. Both will work for a casual email user but if you’re looking for a business use case and advanced email account settings, you should do a bit more research – and we’ll help with that.
What are email clients?
Email clients are software applications that are installed on your device to manage the email that you send and receive. The client interacts with a remote email server to access this email. Apple Mail and Microsoft Outlook are two examples of popular email clients that you have probably heard of. There are additional email accounts that we will discuss in a moment.
What is webmail?
Webmail refers to a type of email that is accessed exclusively online and exists primarily on the cloud rather than on your device. Rather than an installed application or software program that fetches your email, you will manage your inbox from your internet provider. If you’re managing a high volume of correspondence, additional web services like Clean Email can simplify the process by helping you organize and manage emails in bulk. Some common examples include Gmail (as a part of Google Workspace), Hotmail, iCloud Mail, AOL Mail and Yahoo Mail.
Difference between email clients and webmail
Before getting into the different protocols that are used to download emails, it’s a good idea to have an understanding of the main differences between email clients and webmail. If you have ever started an online email account using Outlook.com or Gmail, for example, you have used webmail.

On the other hand, if you use an app for your emails like Microsoft Outlook or Windows Live Mail, this is an email client. Both email clients and webmail send and receive email using similar methods.
Webmail services are apps that have been written to be operated online through a browser with no additional software or applications needed. On the contrary, an email client is an app that will be installed on a local device such as your smartphone or PC.
This client app then interacts with remote email servers to download and send emails.
Whether you’re looking for personal or business use cases, webmail services like Yahoo Mail, Proton Mail, and iCloud seem to be good choices. Also, some webmail providers such as Gmail offer additional services such as Google Drive, additional email storage space, two-factor authenticatio, and more.
What are the different types of email Accounts?
If you have an email account for your business, you probably have one of the three main email account types: POP, IMAP, and Microsoft Exchange.
POP accounts
POP stands for ‘Post Office Protocol’. It was developed many years ago so that email clients such as Outlook could download and send messages from various email services. Over the years, there have been many different versions of POP. POP3 is the most widely used.
A POP email account basically works by downloading email data to the first client to connect to it. This means that if you go on your iPad and open Outlook to download new emails using POP, your iPad is now the only place where they are stored.
They won’t show up if you access the same email address from another device like smartphone or desktop client. This has advantages and disadvantages.
About POP3
Post Office Protocol offers a method of interacting with mail servers that date back to when the internet was quite different to what we are used to today. Back then, most computers didn’t have permanent internet access – instead, users would connect to the internet, use it for whatever they needed to do, and then disconnect.
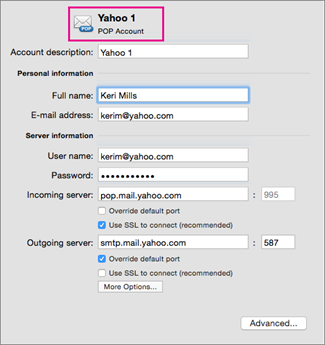
Basic POP account settings. Source
POP was created by engineers as a simple and effective way to download emails to read offline. The first version was developed back in 1984, and it was revised, and POP2 was developed in 1985.
POP3 came later and is still the current version of this email protocol style. It still remains one of the most popular email protocols.
IMAP account
After POP had been used for some time, IMAP or Internet Message Access Protocol was created. Unlike a POP email account, IMAP email accounts continue connecting to the mail server.
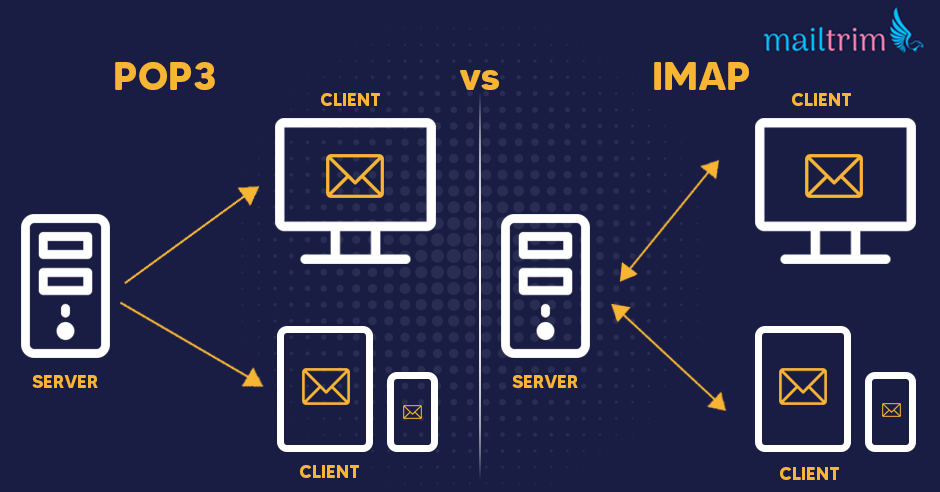
This means that if you open an email client on your laptop computer and download a new email, that email will also be downloaded on your other devices, such as your smartphone.
If you access your emails on your iPad, for example, and read new email messages, it will continue to show as read when you next access your emails from your desktop PC. However, while IMAP is a better option for syncing, it does take up more processing power and can be more error-prone.
Benefits of Using IMAP
There are several benefits of using an IMAP email account, including:
Backup: You will always be able to access your emails on another device if your main device is lost, broken, or stolen, and you can no longer access your mail from it.
Ease of Access: Setting up and using an email address through an IMAP mail account does not require licensing.
Remote Access: Messages remain on the server until you delete them from it, meaning that you do not need to download any mail to your device to view it. Attachments that you do not need to use do not have to be downloaded.
Multiple Device Support: Today, IMAP email accounts are widely supported by most available devices allowing you to easily check your email from PC computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets, and more.
Flexibility: You can easily switch between email clients, webmail, and different devices without losing any messages or having to download them.
Organization: IMAP email accounts allow you to easily organize the inbox according to your needs, including adding folders, sorting messages, marking messages, and more. They also include search features that allow you to find any necessary messages.
Microsoft Exchange
This type of email account is the most advanced and was designed for modern businesses, although many individual users also take advantage of it. The Exchange protocol was developed to allow email users to sync not just emails but also calendars, contacts, and more between email clients and services.
Other Options?
There are other protocols for sending, receiving, and using email services. However, most people use POP3, IMAP, or Exchange, which are the three major protocols used today.
Which To Use When Setting Up an Email Account?
Choosing the right email protocol might be something that you need to consider when setting up a new email account. The good news is that it can be fairly easy to narrow down which might be the best choice for you, depending on your style of communicating with your email service providers and your preferred email settings.
IMAP is the best choice if you check your email from various different devices, including computers, smartphones, and tablets, or use a webmail service. If you mostly use webmail and want this to be synced to your phone or tablet, IMAP is the best way to achieve this.
IMAP is also recommended if you are using one email client on a dedicated machine, although POP3 will also work in this situation.
If you have a huge email history and use an older mail provider without a lot of drive space on offer, POP3 might be the best choice to help prevent you from running out of space on the email server.
On the other hand, if you have a company email address and your workplace uses an Exchange server, then Exchange will be your only option. The exchange might also be an ideal choice if you want your email to sync up with your calendar, contacts, and more.
However, these accounts typically cost more than other types of email addresses, and setting it up and maintaining them can be quite technical.
Office 365 Mailbox Types
Along with the different email protocols, you may also be able to choose from different mailbox types using services such as Office 365. These include:
Licensed Mailbox
A licensed mailbox is designed for personal mail and requires a login. This can either be in the Outlook Web Application or Outlook’s desktop version.
Distribution Groups
Mail that is sent through free distribution groups will be delivered as individual mail items to each destination. Individual group members receive an email in their personal mailbox and can reply from their email address. Similar to mailboxes, you can also set aliases for groups.
Equipment Mailbox
Also known as room mailboxes, equipment mailboxes are free mailboxes for the purpose of reserving and coordinating equipment and rooms.
Shared Mailboxes
Shared mailboxes are free up to 10GB of storage for email and are designed to make it simpler for a group to monitor and send emails from a public email address, such as a business’ customer service email address.
When a person in the group replies to a message that is sent to the shared mailbox, the email will appear to come from the shared mailbox rather than the individual user. The shared mailbox can also be used as a shared team calendar.
No matter what you use an email address for, it’s important to understand the different types of email accounts to choose the right one for you. You should also take a look at the advanced features each account offers, the cloud storage and the overall layer of advanced email security being offered.
Wrapping up
Choosing the right type of email account can seem rather simple. However, if you intend to use email for business and get a good marketing return on investment from this channel, it’s wise to spend some extra time to find the best type of account.
And once you’ve completed that step, you’ll want to make sure the emails you’re sending always reach their intended recipients. This is why you need Bouncer – so you can ensure your mailing lists are clean and free of bogus, disposable email addresses or addresses with typos in them.
Grab your free trial to get started!
Frequently asked questions
What is the best free email account?
It depends on your needs and expectations. Gmail (and the entire Google Workspace) is frequently mentioned as the best all-around choice, especially for offline availability. However, other contenders are just as good in different areas. Yahoo Mail offers a lot of storage, while iCloud mail works flawlessly with iOS devices and the Apple ecosystem.
What is the most secure free email account?
If safety is your main concern, take a look at Proton Mail, Mailfence and Zoho Mail among others. Unfortunately, Gmail is not the top contender on this list. These accounts will not not only protect you from spam emails with their email filters, but they are also great at preventing anyone from getting access. For secure business email, these are some of the top choices.
Is sending emails safer than making phone calls?
In general, yes. There are plenty of ways for other people to intercept a phone call and for someone else to hear what you are saying on the phone. On the other hand, your average Gmail address is very difficult to hack into compared to the effort of listening in on a phone call.

